
What is Cavi Lipo?
The ultrasound cavitation is the mechanism for lipolysis (break down of fat cells) hence the name Cavi-Lipo used in the field of aesthetic medicine is an innovative technique for a non-surgical reduction of the localized fat and cellulite, without injury to skin, vessels, nerves, or connective tissue. Cavi Lipo is a very smart and quick way to reduce stubborn fat which doesn’t go with conventional exercise and diet method of weight loss. This is because it converts the fat into liquid and then is naturally eliminated via urine or metabolized in the body, when followed by lymphatic drainage; the process is faster and is very effective Other names for Ultrasound Cavitation fat loss mechanism are Ultrasound Lipolysis or Cavitation Lipolysis.
Benefits of Cavi Lipo over other Fat Loss Methods Such as Liposuction or Surgery
CAVI LIPO IS:-
- Extremely Comfortable
- Pain Free (As Its Non Invasive)
- No Anesthesia Required
- No Down Time Can Resume Normal Activity Immediately
- Stubborn Localized Fat Removal
- Cellulite Reduction
- Skin Tightening And Rejuvenation
- Improves Lymphatic Drainage
HOW IT WORKS
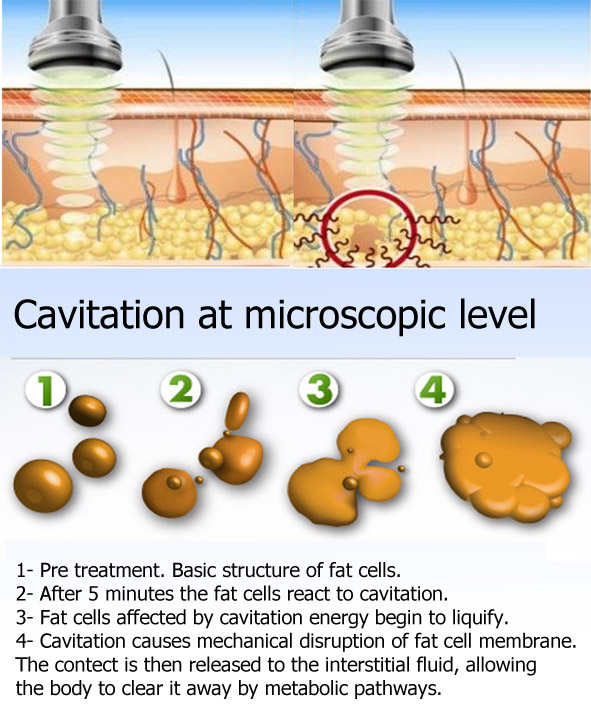
With the Cavi Lipo, the fat cells are exposed to a pressure that breaks the cell membrane, un-leashing the adipose fat deposit destruction. The fat contained (triglycerides) fragments into di glycerides is dispersed into the interstitial fluid among the cells and then cleared via the lym-phatic system and transported through the vascular system to the liver.
Where, fat metabolized by the lipase enzyme into glycerol and free fatty acids, Glycerol is phosphorylated and transported through the vascular system.
The 3-free fatty acids are bound to each albumin molecule and transported to the liver. Fat me-tabolites were processed in the liver in the same manner as fat originating from digested fat. Therefore, the liver makes no distinction between fat coming from the cavitation and fat originating from consumed food both are expelled via the urinary system
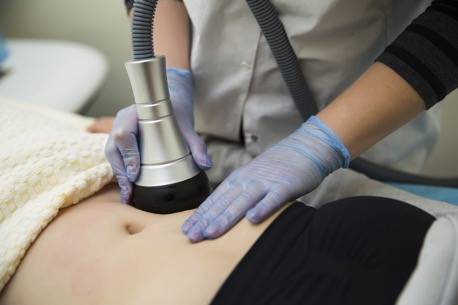
HOW IS CAVITATION FORMED IN FAT CELLS
Ultrasound, as all sound waves, are an alternation of high and low frequency waves. This alternation causes cavitation or formation of cavities (bubbles). During the low frequency phase, these bubbles grow, whereas in the high frequency phase they are compressed and therefore implode. Imploding, they cause a temperature rise with pressures and heat exchange which take place in microsecond time fractions. In the fat tissue, cavitation can contribute, together with the other typical effects of cavitation (thermal, mechanical and chemical) to modify cell membranes with the formation of micro-pores which helps the lipids to pour out, allowing dispersion of triglycerides into interstitial space and lymphatic vessels. It is conceivable that triglycerides can then be absorbed and metabolized by endogenous lipase to glycerol and free fatty acids and incorporated in the total lipoprotein pool.
The Cavi Lipo Process
Body Areas Where Cavi Lipo can be done
- Stomach And Protruding Belly
- Sides Of Waist (Love Handles)
- Hips ( Buttocks)
- Saddle Bags ( Sides Of Thighs )
- Inner Thghs
- Knee Rolls
- Bra Folds
- Arms
- Double Chin
WHEN TO EXPECT RESULTS?
- A minimum of 2 sessions per week are required for a peroid of 6 weeks to see good results.
- Total 12 sessions per body part are needed. However, the exact number of sessions for desired results will be decided by our doctor prior to the
- treatment.
- Each area(measured 15 x 15 cm) is treated for 15 mins, also therapy time depends on the thickness and location of fat layer.
- At one time multiple areas can be chosen
- Can be combined with other therapies for better results
Are There Any Side Effects?
Other than a little redness sometimes around the localized target areas, ultrasound cavitation is completely safe with no known side-effects. It does not affect the blood vessels, nerves or con-nective tissue.
Scientific Research Studies on Ultrasound Cavitation
Focused Ultrasound Lipolysis In The Treatment of Abdominal Cellulite (Moravvej et al, 2015)
In this study total 194 focused Ultrasound Cavitation lipolysis were performed on abdominal area of 28 subjects, weekly for a maximum of 8 sessions each. An average decrease of circumference value of 1.89 cm (95% CI: 1.63-2.02 cm) was estimated for each session of treatment, that was statistically significant (P < .001) (7). Furthermore, there was no significant correlation between per-session circumference reduction and the patient’s age (r = 0.015, P = .954), baseline abdominal circumference (r = 0.350, P = .068) as well as BMI (r = 0.378, P = .134). When compared the weights pretreatment and weight post treatment indicated no significant difference (P > .05), in some cases an increase in the mean value of weight was observed in the next follow-up (71.6 kg vs 88.0 kg, P > .05) (7). No dietary changes were induced during the treatment process in order to eliminate the effect of weight loss on final results. Therefore in this study abdominal fat was reduced by ultrasound cavitation irrespective of any other dietary changes.
Histological and Ultrastructural Effects of Ultrasound-induced Cavitation on Human Skin Adipose Tissue. (Bani et al. 2013)
This study strongly concludes that the noninvasive transcutaneous ultrasound cavitation is a promising and safe technology for localized reduction of fat and provides experimental evidence for its specific mechanism of action on the adipocytes.
Study results showed that Ultrasound cavitation induced a statistically significant reduction in the size of the adipocytes (P < 0.001), the appearance of micropores and triglyceride leakage and release in the conditioned medium (P < 0.05 at 15 min), or adipose tissue interstitium, without appreciable changes in microvascular, stromal, and epidermal components and in the number of apoptotic adipocytes. Clinically, the ultrasound treatment caused a significant reduction of abdominal fat. Therefore, Ultrasound cavitation is the most effective mechanism for noninvasive fat reduction Ultrasonic energy can be delivered by nonfocused or focused waves. With the nonfocused mode, due to depth-related ultrasound attenuation, the superficial skin is exposed to maximum energy intensity. By contrast, focused ultrasound can be concentrated in a defined subcutaneous area to produce clinically relevant fat lysis, while limiting damage to blood vessels, nerves, connective tissue, and the underlying organs.
Immediate effect and safety of HIFU single treatment for male subcutaneous fat reduction. (Guth et al. 2018)
This study was performed on twenty-four male subjects (18 to 59 years old) with BMI ≤ 30 kg/cm² and at least 2 cm of abdominal fat received a single treatment session of High intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU)(6). Along with abdominal before and after measurements, biochemical analyses of blood samples were also performed to assess possible inflammatory effects or oxidative stress induction by the treatment. Results showed a significant decrease (0.6%) in infraumbilical (below naval) circumference of subjects with single treatment when compared with control subjects. Whereas, the laboratory parameters did not present any appreciable changes. Concluding and further strengthening the current view that HIFU is an effective and safe tool for localized fat reduction.
Although many other research studies and evidences can be found on various aesthetic and International scientific journals and medical websites, the above findings suggest that ultrasound cavitations treatment reduced the adipose tissue by changing the permeability of fat cell without causing cellular necrosis. Test results showed that, for ultrasound cavitations treatment, local fat pad thickness was decreased but the weight change was limited. However, with the combined treatment, both local fat pad thickness and body weight were significantly decreased.
click here for appointment
For any further questions contact us or schedule an appointment
References
- Women Sabbour A., Omar H., and El-Banna A.S.,(2009). The Efficiency of Cavitation Ultrasound Therapy on Visceral Adiposity in Perimenpausal. Bull. Fac. Ph. Th. Cairo Univ., Vol. 14, No. (1) Jan. 2009 93
- Ter- Haar, G. and Coussios, C.(2007) “High intensity focused ultrasound: physical principle and devices”. Int J Hyperthermia, 23: 89–104, 2007.
- Garcia-Murray, E., Rivas, O.A. and Stecco, K.A (2005) “The use and mechanism of action of high intensity focused ultrasound for adipose tissue removal and non-invasive body sculpting”. Presented at the American Society of Plastic Surgery Annual Meeting. Chicago (IL).
- Zhou, B., Leung, B., & Sun, L. (2017). The Effects of Low-Intensity Ultrasound on Fat Reduction of Rat Model. BioMed research international, 2017, 4701481. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4701481
- Bani, D., Quattrini Li, A., Freschi, G., & Russo, G. L. (2013). Histological and Ultrastructural Effects of Ultrasound-induced Cavitation on Human Skin Adipose Tissue. Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Global open, 1(6), e41. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0b013e3182a7f222
- Guth, F., Bitencourt, S., Bedinot, C., Sinigaglia, G., & Tassinary, J. (2018). Immediate effect and safety of HIFU single treatment for male subcutaneous fat reduction. Journal of cosmetic dermatology, 17(3), 385–389. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12466
- Moravvej, H., Akbari, Z., Mohammadian, S., & Razzaghi, Z. (2015). Focused Ultrasound Lipolysis in the Treatment of Abdominal Cellulite: An Open-Label Study. Journal of lasers in medical sciences, 6(3), 102–105. https://doi.org/10.15171/jlms.2015.02

